15. Electromagnetic Induction
- Magnitude of the Induced Potential Difference (10 min)
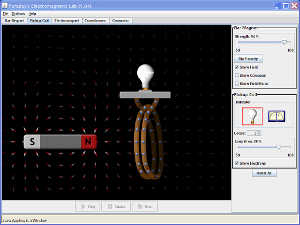
- Simulation: Faraday’s Electromagnetic Lab (Select “Pickup Coil” tab)- Move a magnet in and out of a loop circuit that contains a lightbulb. Be aware that the blue dots shown in the wire are electrons, not the positive charge of conventional current.
Predict and then test your predictions using the simulation: Which way will the electrons in the wire move when…
- The magnet is not moving
- The magnet is moving to the right, and the N pole is moving into the loop?
- The magnet is moving to the right, and the S pole is moving out of the loop?
- The magnet is moving to the left, and the S pole is moving into the loop?
- The magnet si moving to the left, and the N pole is moving out of the loop?
- Simulation: Faraday’s Law – Observe the direction and magnitude of induced current on the galvanometer for different motions of the magnet in and out of the coil. Select “Show magnetic field lines” to visualize the magnetic flux. (Important: The meter shown is incorrectly labeled “voltage”; It is actually a galvanometer measuring CURRENT.) A positive current corresponds to a counter-clockwise conventional current in the coil. To do: (1) Predict whether the current will be positive or negative for different motions of the magnet. (2) Compare the amount of current induced in coils with different numbers of loops. (3) How can you get the largest current flowing in the wire?